mb
Introduction to MB
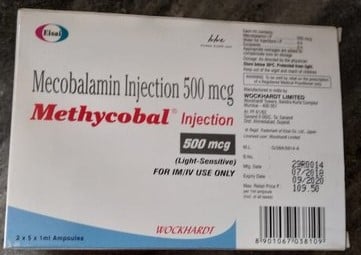
MB, also known as Methylcobalamin or Mecobalamin, is a form of Vitamin B12 that plays a vital role in the body's functioning. It is essential for nerve health, brain function, and the production of red blood cells. Unlike other forms of Vitamin B12, MB is directly involved in cellular metabolism and DNA synthesis, making it a preferred choice for treating Vitamin B12 deficiency. MB is available in various forms, including tablets, injections, and capsules, providing flexibility in its administration to suit different patient needs.
Composition of MB
The primary active ingredient in MB is Methylcobalamin, a bioactive form of Vitamin B12. Methylcobalamin is crucial for maintaining healthy nerve cells and supporting neurological function. It is directly involved in the synthesis of myelin, the protective sheath around nerves, which enhances nerve signal transmission. Additionally, Methylcobalamin aids in the production of red blood cells and DNA, contributing to overall cellular health and energy production. By offering a readily absorbable form of Vitamin B12, MB ensures effective treatment of deficiencies and supports optimal health.
Uses for MB
- Management of Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Support for nerve health and function
- Improvement of energy levels and reduction of fatigue
- Enhancement of brain function and cognitive performance
- Support for red blood cell production
Side Effects of MB
- Allergic reactions (rash, itching, swelling)
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Headache
- Dizziness
Precautions for MB
Before using MB, it is essential to inform your healthcare provider if you have any allergies, pre-existing medical conditions, or are taking other medications. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult a doctor before starting MB. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and not exceed the recommended amount. In case of any adverse reactions, seek medical attention immediately. Regular monitoring of Vitamin B12 levels may be necessary to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment.
Specifications of MB
MB is available in various forms to cater to different patient needs:
- Tablets: Easy to administer and suitable for daily use.
- Injections: Used for more immediate absorption and in cases of severe deficiency.
- Capsules: Provide an alternative oral form with similar benefits to tablets.
Conclusion
MB, or Methylcobalamin, is a crucial form of Vitamin B12 that supports nerve health, brain function, and red blood cell production. Available in tablets, injections, and capsules, MB offers flexibility in administration to meet diverse patient needs. With its essential role in cellular metabolism and DNA synthesis, MB is an effective treatment for Vitamin B12 deficiency. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement or medication to ensure safety and efficacy.
Similar Medicines
More medicines by Saimed Formulations
Available in 2 variations

MB 500mcg Injection
vial of 1 ml Injection

MB 12 Injection
ampoule of 1 ml Injection
Disclaimer : This information is not a substitute for medical advice. Consult your healthcare provider before making any changes to your treatment . Do not ignore or delay professional medical advice based on anything you have seen or read on Medwiki.
mb
Prescription Required
Manufacturer :
Saimed FormulationsComposition :
methylcobalamin/mecobalamin













.svg)
